Immunology -Immunology Definition
Immunology | Internal defence is carried out by White blood cells, macrophages, inflammatory response and interferons. Immune system acts as warrior of the body creating internal support of body.Various Immunity providing units are described below:
White Blood Cells
The leukocytes in general and lymphocytes in particular squeeze out through the wall of the blood capillaries into the extra-vascular regions. This phenomenon is called Diapedesis.
Lymphocytes:- Produce plasma cells which secrete antibodies to provide immunity.
Monocytes:- They are so phagocytic in action.
Eosinophils:- They can attach themselves to parasitic forms and cause their destruction by liberating lysosomal enzymes on their surface.
Neutrophils:- They are also phagocytic in nature.
Macrophages:- They are formed by the enl argement of monocytes.
Inflammatory response
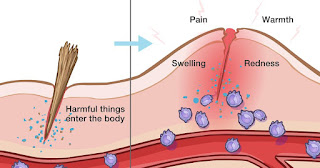
When the microorganisms enter the body tissue through which some injury, these produce some toxic substances which kill body cells. These broken cells release sone chemicals which attract the mast cells.
The mast cells release Histamine.
Histamine causes dilation of capillaries and small blood vessels surrounding the injury and increases the permeability of the capillary walls. This results in increased blood flow which results in swelling in the area, redness, etc.
Interferon :- They are the proteins released by the body cells in response to a viral infection.
Antigens:- These are the foreign 'molecules'
that invade the body of an organism.
Antibodies:- They are the substances produced by the immune system to defend against the antigens.








No comments:
Post a Comment